Eigen
Take a vector and rotate it back around a point
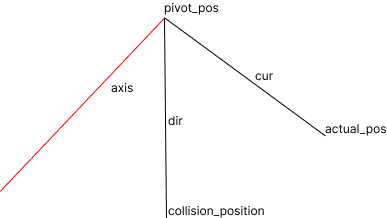
1.Compute the rotation axis of two vectors
const Eigen::Vector3f dir = static_cast<Eigen::Vector3f>(*pivot_pos) - static_cast<Eigen::Vector3f>(collision_position_);
const Eigen::Vector3f cur = static_cast<Eigen::Vector3f>(*pivot_pos) - static_cast<Eigen::Vector3f>(actual_pos_);
Eigen::Vector3f axis = cur.cross(dir);
2.Compute the Angle between two vectors
axis.normalize();
const float angle = std::acos(cur.normalized().dot(dir.normalized()));
const float angle_in_degrees = static_cast<float>(angle * (180.0f / M_PI));
Perform a rotation around the point
Eigen::Vector3f pos(actual_pos_.x, actual_pos_.y, actual_pos_.z);
Eigen::Quaternionf qua(actual_rot_.w, actual_rot_.x, actual_rot_.y, actual_rot_.z);
const Eigen::Vector3f pivot(pivot_pos->x, pivot_pos->y, pivot_pos->z);
ApplyRotation(pos, qua, pivot, axis, angle_in_degrees);
actual_pos_.x = pos.x();
actual_pos_.y = pos.y();
actual_pos_.z = pos.z();
actual_rot_.w = qua.w();
actual_rot_.x = qua.x();
actual_rot_.y = qua.y();
actual_rot_.z = qua.z();
static void ApplyRotation(Eigen::Vector3f &position, Eigen::Quaternionf &rotation, const Eigen::Vector3f &pivot_pos, const Eigen::Vector3f &axis, float angle) {
// Convert the Angle from degrees to radians
const float angle_in_radians = static_cast<float>(angle * M_PI / 180.0f);
// Creates a rotated quaternion
const Eigen::Quaternionf rotation_quaternion(Eigen::AngleAxisf(angle_in_radians, axis));
// Computed position change
Eigen::Vector3f translatedPosition = position - pivot_pos;
translatedPosition = rotation_quaternion * translatedPosition;
position = pivot_pos + translatedPosition;
// update direction
rotation = rotation_quaternion * rotation;
}
Decomposition vector
The axis of the model's own coordinate system is obtained, and the force is decomposed into the local coordinate system.
Convert to Eigen representation
const Eigen::Vector3f position(-g_data[6], g_data[7], g_data[8]);
const Eigen::Quaternionf rotation(Eigen::AngleAxisf(DegToRad(g_data[9]),Eigen::Vector3f::UnitX())
* Eigen::AngleAxisf(DegToRad(-g_data[10]), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitY())
* Eigen::AngleAxisf(DegToRad(-g_data[11]), Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ()));
const Eigen::Vector3f scale(scale_, scale_, scale_);
const Eigen::Vector3f force(force_radial.x, force_radial.y, force_radial.z);
The pos,rot and scale of the world coordinate system are represented by a matrix
const Eigen::Matrix4f transform = CreateTransformMatrix(position, rotation, scale);
Decomposition
local_force_ = TransformForceToLocal(force, transform);
static Eigen::Matrix4f CreateTransformMatrix(const Eigen::Vector3f &position, const Eigen::Quaternionf &rotation, const Eigen::Vector3f &scale) {
Eigen::Matrix4f transform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
transform.block<3,3>(0, 0) = rotation.toRotationMatrix() * scale.asDiagonal();
transform.col(3).head<3>() = position;
return transform;
}
You convert the force from the world coordinate system to the local coordinate system, and you invert the matrix of the world coordinate system
static Eigen::Vector3f TransformForceToLocal(const Eigen::Vector3f &force, const Eigen::Matrix4f &transform) {
// Inverse transform for converting from global to local
const Eigen::Matrix4f inverse_transform = transform.inverse();
const Eigen::Vector4f force_homogeneous(force[0], force[1], force[2], 0);// Force as a 4D vector for matrix multiplication
Eigen::Vector4f local_force_homogeneous = inverse_transform * force_homogeneous;
return Eigen::Vector3f(local_force_homogeneous[0], local_force_homogeneous[1], local_force_homogeneous[2]);
}
Then define the three axes of the local coordinate system
// Define local coordinate Axis of X Y Z
const Eigen::Vector3f x_axis(1, 0, 0);
const Eigen::Vector3f y_axis(0, 1, 0);
const Eigen::Vector3f z_axis(0, 0, 1);
Then compute the vector on the XYZ axis
// Compute the vector on the XYZ axis
Eigen::Vector3f force_on_x = local_force_.x() * x_axis;
Eigen::Vector3f force_on_y = local_force_.y() * y_axis;
Eigen::Vector3f force_on_z = local_force_.z() * z_axis;
To render debug view, convert these vectors into the world coordinate system
// Converts the local vector back to the world coordinate system
Eigen::Vector4f force_on_x_world = transform * Eigen::Vector4f(force_on_x[0], force_on_x[1], force_on_x[2], 0);
Eigen::Vector4f force_on_y_world = transform * Eigen::Vector4f(force_on_y[0], force_on_y[1], force_on_y[2], 0);
Eigen::Vector4f force_on_z_world = transform * Eigen::Vector4f(force_on_z[0], force_on_z[1], force_on_z[2], 0);
Finally, assign values to the three forces
force_on_world_x_.x = force_on_x_world.x();
force_on_world_x_.y = force_on_x_world.y();
force_on_world_x_.z = force_on_x_world.z();
force_on_world_y_.x = force_on_y_world.x();
force_on_world_y_.y = force_on_y_world.y();
force_on_world_y_.z = force_on_y_world.z();
force_on_world_z_.x = force_on_z_world.x();
force_on_world_z_.y = force_on_z_world.y();
force_on_world_z_.z = force_on_z_world.z();
Last modified: 02 July 2024